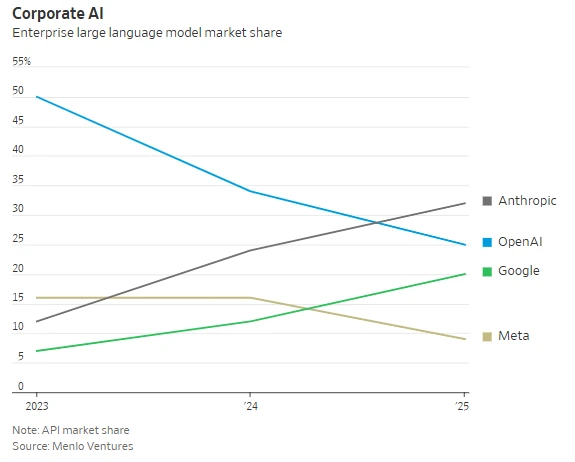
According to media reports, on December 14th local time, a "sweeping robot" iRobot, the pioneer of the industry, has officially filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in a Delaware court.
iRobot expects to complete the aforementioned procedures by February 2026. Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the United States is a reorganization-type bankruptcy procedure for companies. Its core purpose is not to directly liquidate and close a company, but to give companies that are in financial distress but still have operational value a chance to "breathe and be reborn".
According to iRobot's announcement, it has entered into a Restructuring Support Agreement with its secured creditors and major contract manufacturers , Shenzhen PICEA Robotics Co., Ltd. and Santrum Hong Kong Co., Limited (collectively referred to as "Picea"). Picea has R&D and manufacturing bases in China and Vietnam and employs more than 7,000 people worldwide.
Under the terms of the Restructuring Support Agreement, Picea will acquire 100% of iRobot's equity. iRobot stated that this arrangement will significantly improve iRobot's balance sheet, ensure the company can maintain normal operations, and preserve its global business footprint.
iRobot CEO Gary Cohen said, "This transaction will strengthen our financial position and ensure business continuity for our consumers, customers and partners."
The company emphasized that iRobot will maintain normal business operations during the bankruptcy proceedings, and its app functionality, customer service programs, global partnerships, supply chain collaborations, and in-transit product support will not be affected. To ensure business continuity, iRobot has filed a series of routine motions with the court to ensure that the company can operate as usual, including fulfilling commitments to employees and making timely and full payments to suppliers and other creditors to amounts owed before, during, and after the commencement of the proceedings.
Once the court approves the transaction, iRobot will become a wholly owned private company under Picea's ownership structure, and its common stock will no longer be listed on Nasdaq. Or any other national securities It is listed and traded on the exchange.
The company anticipates that if the court ultimately approves the Chapter 11 bankruptcy reorganization plan, existing common shareholders will not be able to obtain any equity in the reorganized company; all issued and outstanding shares of the company will be cancelled, and common shareholders will face a total loss of their investment and will not receive any compensation.

Image source: iRobot robotic vacuum cleaner (website)
iRobot's financial troubles: Losses and insolvency.
On December 1, local time in the United States, iRobot's official website disclosed a document submitted to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, which revealed that iRobot is currently facing an extremely serious crisis.
Facing a severe liquidity crisis and debt default risk, Picea, iRobot's main contract manufacturer, acquired $191 million in outstanding loans from iRobot through its subsidiary Santrum , becoming its main creditor. This new creditor, Picea, is actually a supplier from Shenzhen, China—Shenzhen Shanchuan Robotics Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Shanchuan).
Back in March 2025, iRobot announced that it was evaluating several options, including but not limited to considering asset sales or strategic transactions, as well as refinancing its debt.
However, by late October, a potential buyer ultimately chose to withdraw after lengthy and exclusive negotiations.
At this point, a new creditor emerged in the documents: Picea—a major collaborating manufacturer of iRobot, Sugikawa.
On November 24, 2025, Sugikawa, through its subsidiary Santrum, received compensation from the original creditor, Carlyle Group. The related party acquired $191 million in outstanding loans (principal + interest) from iRobot, thus becoming iRobot's major creditor. In addition, as of the same period, iRobot owed Sugikawa $162 million in product manufacturing costs, of which $90.9 million was overdue.
This also means that iRobot currently owes Sugikawa over $350 million, or about 2.5 billion yuan, while iRobot's total cash and cash equivalents amount to only $24.8 million.
According to iRobot, it is currently in discussions with Sugikawa regarding a mutually agreed-upon solution aimed at resolving the company's outstanding payments to Sugikawa and seeking alternative funding to maintain daily operations.
iRobot's liquidity crisis is imminent. In its 2024 financial report, the auditors included a descriptive paragraph expressing significant doubt about iRobot's ability to continue as a going concern. According to the relevant credit agreements, iRobot still requires Sugikawa to grant credit extension permission; otherwise, it would constitute a credit default, potentially forcing iRobot to drastically reduce or cease operations and possibly file for bankruptcy protection.
According to its Q3 2025 financial report, iRobot's revenue was only $146 million, a 24.6% decrease compared to the same period in 2024. Furthermore, its profit turned from a profit of $15.1 million in the same period last year to a loss of $9.9 million. iRobot also acknowledged that its 2026 financial report still requires continued waivers from Sugikawa.
It is understood that Sugikawa is currently iRobot's single contract manufacturer. iRobot stated, "Our business and operational results depend to a large extent on the manufacturer's ability to continue production."
Once a globally renowned company, iRobot's fate is now firmly in the hands of a low-profile Chinese manufacturer.
The Wind Rises in 2022: A Critical Juncture from Glory to Mire
Founded in 1990, iRobot is a leading global consumer robotics company. It launched its first Roomba robotic vacuum cleaner in 2002, which is considered the "grandfather" of robotic vacuum cleaners in the industry. The company went public on NASDAQ in 2005.
iRobot's founder is Rodney Brook , a professor at MIT. S, Colin Engle, and Helen Greiner. From the outset, they aimed at the broader robotics field, rather than limiting themselves to robotic vacuum cleaners.
"At that time, we decided to establish a company focused on producing practical robots," Angell, one of the founders of iRobot, told domestic media.
For a long time, iRobot developed many advanced and practical robots, including military robots that could reduce casualties in war, the high-precision "Pyramid Rover" exploration robot, security robots that went deep into the ruins of the World Trade Center to assist in searching for survivors after the 9/11 attacks, and special robots that went deep into the radiation zone of the Fukushima nuclear power plant to help shut down the nuclear reactors. The development and launch of the Roomba robotic vacuum cleaner in 2002 propelled iRobot's rapid commercial growth.
However, in 2022, iRobot's performance took a sharp turn for the worse.
Public data shows that iRobot's revenue in 2022 decreased by 24% year-on-year to US$1.1834 billion (approximately RMB 8.118 billion), and its net profit turned from profit to loss, with a net loss of US$286.3 million.
According to iRobot's 2022 annual report, its revenue in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa decreased by 43% year-on-year, while revenue in the United States decreased by 18% and revenue in Japan decreased by 6%. In the Chinese market, iRobot also faces fierce competition from local Chinese cleaning appliance brands.
According to previous media reports, iRobot once held over 80% market share in the US robotic vacuum cleaner market. However, in a report released by IDC in the second quarter of this year, iRobot's global market share has fallen to 7.9%.
On December 4th, You Danni, a senior expert in the cleaning appliance industry, stated in an interview with NBD that the core reason for iRobot's fall from grace was the rapid development of the cleaning appliance industry in recent years, while iRobot failed to keep pace with the industry's growth, especially during the pandemic, when iRobot was essentially out of sync with the development of the domestic industry. During this period, a large influx of capital into the cleaning appliance industry led to companies like Ecovacs... Chinese cleaning appliance companies such as Dreame and Roborock have experienced rapid growth, driving the rapid upgrading and iteration of robotic vacuum cleaners. After the pandemic, the industry has shown rapid development. In contrast, iRobot is relatively lagging behind in terms of both technology and products.
In 2022, Amazon The company plans to acquire iRobot for approximately $1.7 billion in an all-cash deal, aiming to enhance its smart home capabilities. Equipment stability. However, this acquisition is subject to antitrust scrutiny from the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC), the European Union, and other bodies.
In January 2024, Amazon planned to acquire iRobot for $1.4 billion, a deal that was expected to bring new development opportunities to iRobot. However, the deal ultimately failed due to opposition from EU regulators.

(Source: Daily Economic News)