After the market closed on Wednesday local time, tech giant Nvidia... The company will release its latest quarterly earnings report. According to calculations by analytics firm ORATS, this earnings report implies a two-way fluctuation of approximately 7% in the stock price, equivalent to a market capitalization fluctuation of up to $320 billion.
If this figure materializes, it will rewrite Nvidia's record for the largest post-earnings market capitalization change.
Analysts generally agree that as the core GPU supplier for training large language models and AI applications, Nvidia is not just a chip company, but also an "anchor" for the entire AI capital expenditure cycle. With a weight of nearly 8% in the S&P 500, any signals regarding demand, profit margins, or the supply chain can impact semiconductor companies. To hyperscale data centers From there, to broader market sentiment regarding AI infrastructure.
Chris Murphy, co-head of derivatives strategy at brokerage firm Susquehanna, bluntly stated: "Nvidia's impact goes far beyond market capitalization fluctuations; it determines whether we enter the next round of expansion or begin to digest the previous gains."
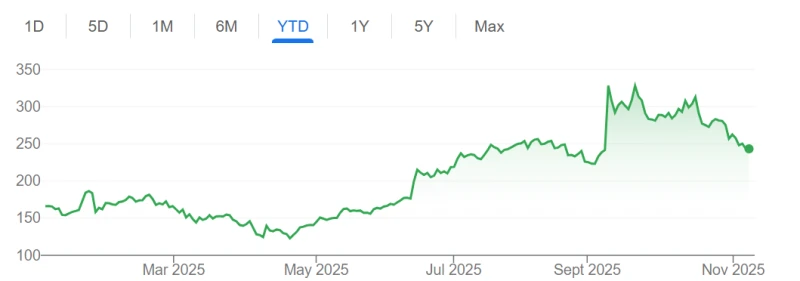
Over the past two weeks, tech stocks have retreated due to valuation pressures, with Nvidia's stock price falling about 10% from its all-time high at the end of October. Some well-known investors, including Peter Thiel's fund and SoftBank, have also recently reduced their Nvidia holdings, making the market more focused on whether this earnings report can answer a fundamental question: Is the AI craze accelerating or cooling down?
Nvidia achieves "key pricing" in the AI cycle.
The market generally expects Nvidia to report strong revenue, but the key is not the growth rate itself, but management's assessment of demand, supply chain and customer investment pace.
Murphy believes that if Nvidia releases any signal about slowing down its AI procurement pace, the impact will not only be on the chip sector, but also on data centers , server supply chains, and related software ecosystems. "Even if Nvidia's stock price only moves by 7%, the narrative impact could extend to deals worth up to $10 trillion."
Jason Pride, head of investment strategy at wealth management firm Glenmede, said that Nvidia's earnings report has transformed from a "fundamental event" into a "macroeconomic variable." He emphasized, "AI is no longer just a technology story; it has become an economic engine, and Nvidia is its igniter."
A key contradiction in the current market is that capital expenditures are unprecedented, but productivity gains have yet to materialize.
According to media reports on the capital expenditures of major tech companies, Amazon... , Microsoft Google, Oracle Meta plans to invest approximately $400 billion in data centers this year, nearly double last year's figure.
Deutsche Bank According to forecasts, with the rapid expansion of AI computing power and data center capacity, related infrastructure investment will reach approximately $4 trillion over the next five years.
However, the forecasts for productivity gains vary widely, ranging from 0.1% to 2.9% annualized, highlighting the uncertainty surrounding whether the commercial returns from AI will arrive on time.
Since ChatGPT's release, global stock market capitalization has increased by over $17 trillion, a significant portion of which has been driven by AI narratives. However, investors are now re-evaluating whether this round of investment can generate sustainable returns, rather than being a one-off valuation surge.

Capital concentration, energy pressure and regulatory concerns
Nvidia's financial report is not only seen as a window into demand and profitability, but also sparks discussions about the sustainability of AI infrastructure.
Currently, AI computing power supply and cloud services are highly concentrated. Synergy Research data shows that AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud together account for over 60% of the global cloud infrastructure market; Nvidia controls over 90% of the high-end AI chip market. market.
Meanwhile, the energy pressures brought about by the expansion of computing power are already evident. A report from the Virginia Department of Energy shows that data centers in Northern Virginia account for nearly a quarter of the state's electricity consumption, raising concerns among regulators about the grid's capacity and the region's energy structure.
Analysts believe that the rapid expansion of AI infrastructure is accumulating new industry risks. Electricity demand is climbing at an abnormal rate, with data center energy consumption becoming the largest source of incremental electricity consumption in some US cities; at the same time, tech giants are borrowing heavily in the bond market to support data center expansion plans, increasing financing pressure; regulators are also becoming more vigilant, with both the US and the EU focusing on the potential "AI bubble" and the systemic risks posed by "too big to fail" companies.
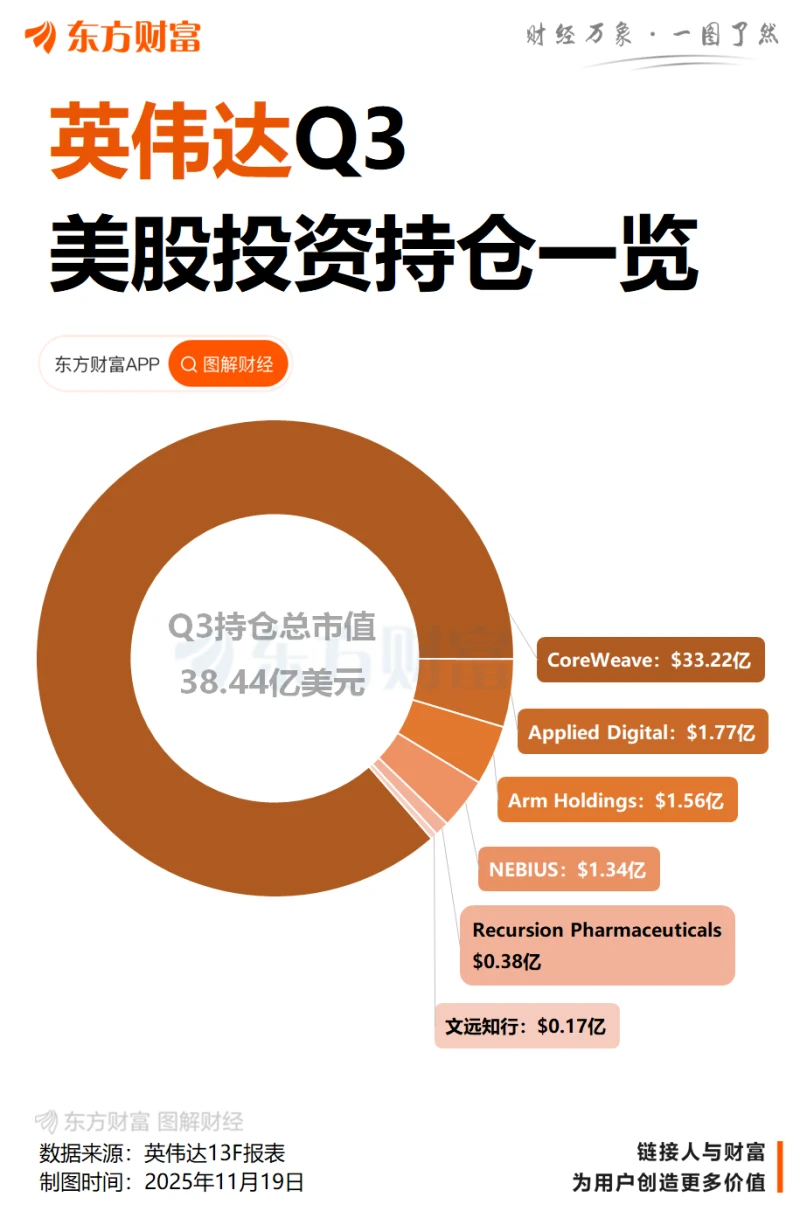
Dongcai Illustrated Guide: Some Useful Tips
(Article source: CBN)